The increased airborne spread of pathogenic microorganisms has raised serious concerns about their threat to human safety.
Beyond this threat, many people wish to protect themselves from an environment that is full of unnoticed pollutants, allergens and many other harmful agents that endanger their long term heallth.
Until now there was no effective method to quickly reduce the risk of pathogens in large airspaces and current solutions (such as HEPA filter) do not solve the risk in environments with people in transit
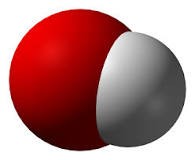
Only the OPEN-AIR FACTOR and its oxidation processes based on hydroxyl radicals (OH●) solve the problem by generating an active germicide in situ, in sufficient and constant quantities to cover a large volume of airspace. This reaction is also effective in neutralizing polluting PM’s, Volatile compounds, Alergens and Unpleasant Odours.

A mechanism is required to successfully sterilize bacteria and viruses. Hydroxyls (OH●) are highly reactive, so they quickly combine with bacteria and viruses, while at the same time removing H atoms and rendering them unable to complete the binding process.
Other radicals OH, F (fluorine), O3 (ozone) and H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) have such reactions, but have toxic substances.
On the other hand, hydroxyls (OH●) are harmless although they have high reactivity. In the case of harmful gases such as VOCs, hydroxyls (OH●) remove these gases through a series of reactions, while bacteria and viruses are neutralized through a single reaction.
The oxidation reaction of hydroxyls (OH●) is billions of times faster and more than 13 times more efficient than that of ozone.

Hydroxyls (OH●) steal hydrogen (H) from proteins on the surface of bacteria, breaking down the proteins.
The combination of a hydroxyl (OH●) with hydrogen (H) creates water (H2O), which returns to the air.
Therefore, a key notion in this disinfection technology is the artificial creation of naturally formed hydroxyls (OH●).
PUROH medical equipment distributed by AOP-TECHNOLOGIES is an ‘indoor air quality solution’ that is completely different from the existing filter-type air purifiers.
The natural air purification method based on advanced oxidation processes has been used as military defense technology in Europe and has been commercialized in European hospitals since the 1990s.
It is the world’s only air sterilization technology that generates long-range hydroxyls (OH●) by reacting a small amount of ozone (O3) with the terpene oil in the cartridge.
Unlike other hydroxyl generation technologies, it is possible to generate a cascade reaction that allows the (OH) to occupy large volumes of space.
Hydroxyl (OH●), a natural cleaning material, is made in two processes. The first takes place in the stratosphere, where high temperatures, high ultraviolet energy, and high ozone work together.
In this case, a high concentration of hydroxyls (OH●) is created, which disinfects various natural contaminants fraom earth. Second, it occurs when vegetable oils (terpenes) from natural plants meets a small amount of naturally occurring ozone; this is one of the reasons why you feel refreshed in the midst of a forest.
Hydroxyl (OH●) is a natural purifying material, it has strong oxidizing power and purifies the atmosphere by itself. In it In the case of multicellular organisms, it is difficult for hydroxyls (OH●) to enter their systems due to the enzymatic mechanism, and for this reason, it is harmless to the human body.
The density of hydroxyls (OH●) in the general atmosphere is 200,000 to 8,000,000 parts/cc.
What is fine dust?
Dust refers to particles of substances that float in the air. It is often generated by burning fossil fuels like coal and oil, or from exhaust gases from factories and cars. Dust is classified into Total Dust (TSP, Total Suspended Particles), which is less than 50 μm, and Fine Dust (PM, Particulate Matter), which has a very small particle size.
Fine dust has very small particles and is divided into PM10, which is general fine dust, and PM2.5, which is also called “ultrafine dust”. If PM10 is about 1/5 ~ 1/7 smaller than the diameter of human hair (50 ~ 70μm), PM2.5 is very small, about 1/20 ~ 1/30 of the hair.
As such, fine dust is so small that it is invisible, so it remains in the air, enters through the respiratory tract, enters the lungs, etc., or travels through blood vessels and enters the body, thereby which can adversely affect health.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has proposed air quality guidelines for fine dust (PM10, PM2.5) since 1987, and in 2013, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has designated fine dust as a Group 1 carcinogen (Group 1 ) that has been confirmed to be carcinogenic to humans.
The composition of the fine dust can be different depending on the region, the season, the climatic conditions and the source.
Natural fine dust is made up of soil, salt, and plant pollen. Man-made fine dust is fumes, exhaust gases and flying dust. The health problem is mainly man-made fine dust.
In general, the components of artificial fine dust are lumps formed by the reaction of air pollutants (sulphates, nitrates, etc.), carbon and fumes generated in the process of burning fossil fuels such as coal and oil, and minerals from the dust of the I usually. on the surface.
Looking at the nationally measured fine dust composition ratio, sulfate and nitrate are the highest with more than 50%, carbon and soot are less than 20%, and minerals are more than 5%.
The new, innovative and disruptive patented technology that manages to efficiently generate and expand hydroxyl radicals (OH·) which, through Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP), inactivate up to 99.9% of pathogenic microorganisms (viruses and bacteria) and at the same time reduce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and PM particles, according to studies carried out by universities and independent laboratories.
Hydroxyl radicals clean the air and surfaces according to a study published in the scientific journal IJOER “International Journal of Engineering Research and Science”, and reduce the presence of environmental pollutants mentioned above.
Using OH· in the atmosphere, the Military Defense developed this technology in the 1970s for CBR (Chemical/Biological/Radiological) warfare. It was marketed in the 1990s in European hospitals. This demonstrates the excellent results in eliminating harmful substances such as bacteria, germs and viruses, harmful gases, mold and respiratory allergens that give rise to a polluted environment.
Within the Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), hydroxyl radicals (OH·), in small concentrations, perform sanitizing functions against viruses, bacteria, allergens and mold, and enable the degradation of organic compounds from the air to mineral forms or harmless water-soluble organic compounds.
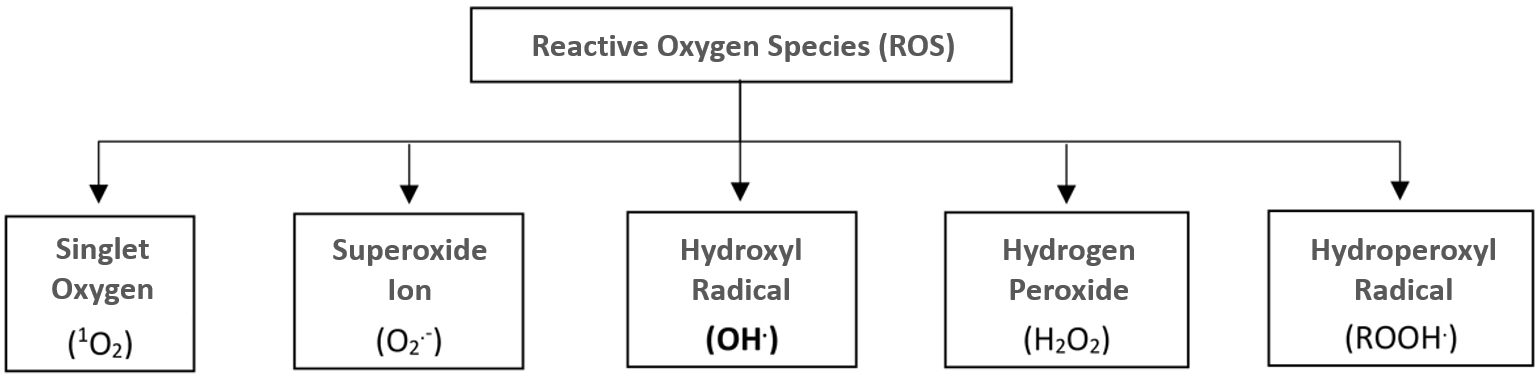
The hydroxyl radical OH· is the most important natural oxidant in tropospheric chemistry. It is often called the “detergent of the atmosphere”, since it reacts with many pollutants, starting the process of purifying them. It also plays an important role in removing greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane.
The importance of Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP) lies in the fact that their application destroys the contaminant. In this way, an almost total mineralization of organic pollutants is achieved, that is, they are applied in the inhibition of the vast majority of organic compounds, especially non-biodegradable compounds such as organochlorines, PCBs, PAHs, etc. It is a clean technology.
Hydroxyl radicals have excellent advantages over the 3 main chemical disinfectants based on chlorine, alkali and ammonium-alcohol-alkali:

Absence of selectivity...
of pathogenic microorganisms due to the high oxidation potential of 2.8V (slightly lower than fluorine 3.08V).
The processing time of the OH· is very short
The chemical reaction speed of OH is 107 times higher than other oxidants such as ozone, peroxide or chlorine.

It is a green oxidizer
That is, hydroxyl radicals break down into water (H2O) and oxygen (O2) with no residual oxidants after their biochemical reactions.
The process of purification and disinfection of air and surfaces through hydroxyl radicals occurs when they come into contact with pollutants, and they react as follows:
Breaks the protection membranes from viruses and bacteria (lipidic reaction):
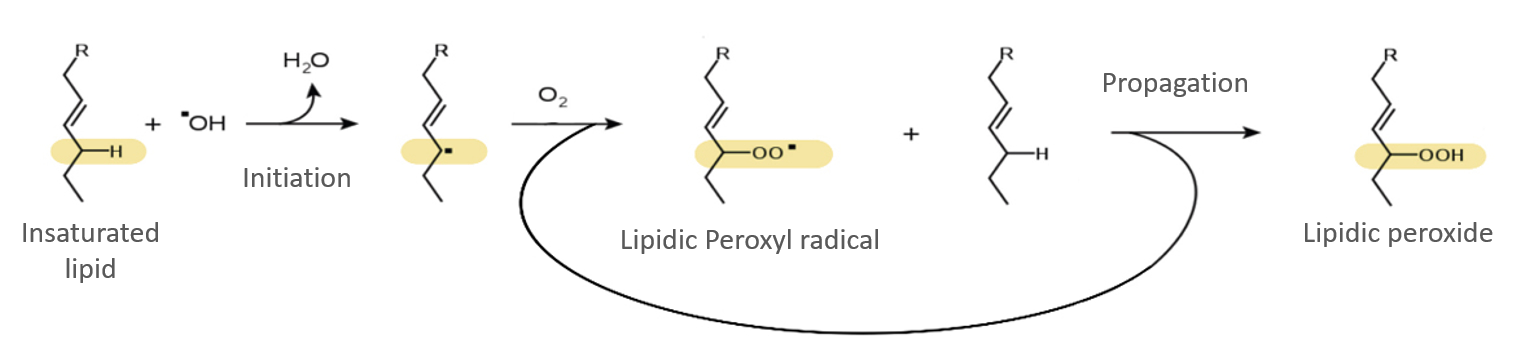
Alters the genetic information of viruses and bacteria (lipid peroxidation reaction):
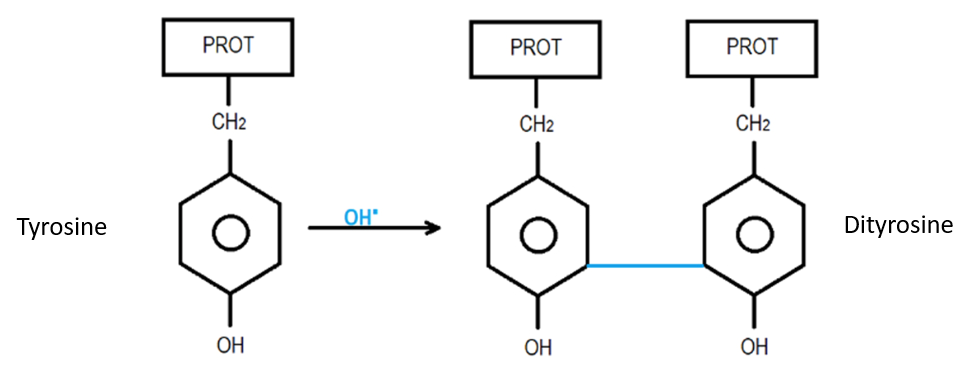
Oxidizes volatile organic compounds vocs in heavier products that precipitate to the soil
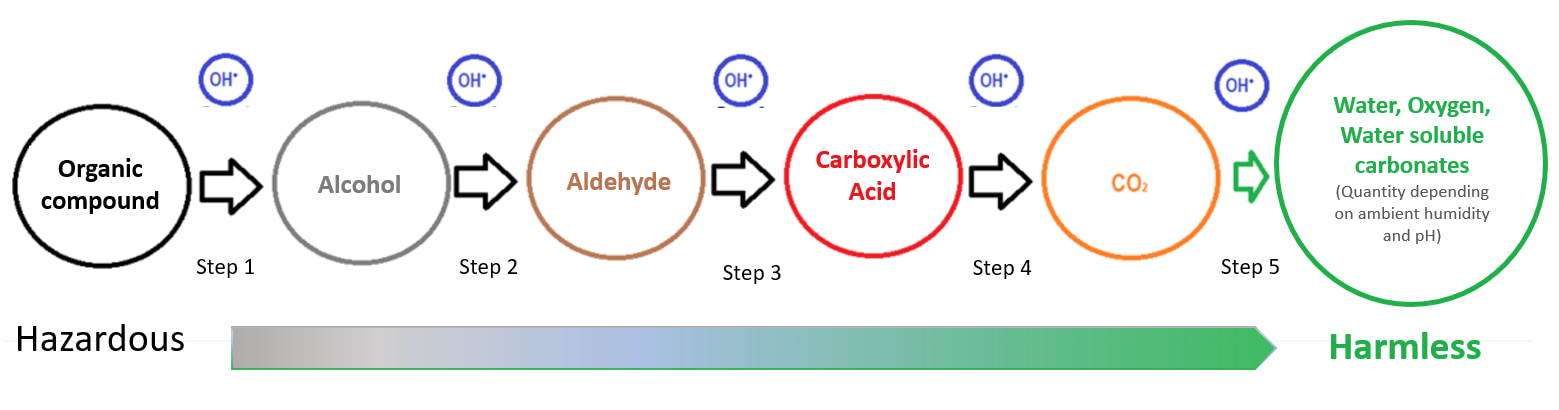
Breaks down the particles suspended in the air.
Once the oxidation process begins, the effect called “respiratory explosion” occurs, which consists of a series of cascading reactions that produce more hydroxyl radicals and thus accelerate the process of eliminating viruses and bacteria.
In this way, OH technology produces a chain effect that efficiently purifies and disinfects the air and surfaces in an area of up to 50-60m 2.
The purifier evaporates carefully standardized amounts of a terpene such as d-limonene or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) from the cartridge, which react with a controlled emission of ozone at low concentrations (<< 0.02 ppm) complying with exposure limits against agents chemicals adopted by the National Institute for Safety and Health that sets them below 0.05 ppm.

The purifier's ozone emission, UL certified by a third-party laboratory, is below the limit concentration emitted by the WHO in the year 2000 Environmental Limit Values (ELVs) for the general public for exposures of up to 8 hours.
Please be patient while we search our data base. Thank you…